The Ruse of the Unemployment Numbers
March 1, 2015 Leave a comment
 Hungry? Imagine being served your multi-course dinner by a Ph. D. in Pharmacology, or getting your burrito delivered by an experienced human resources professional. Both of these scenarios are very real. Both of these individuals, one a friend, the other an acquaintance, lost jobs due to economic downturns at their respective organizations and both have taken jobs, simply to pay the bills, while they seek out new opportunities in their chosen professions.
Hungry? Imagine being served your multi-course dinner by a Ph. D. in Pharmacology, or getting your burrito delivered by an experienced human resources professional. Both of these scenarios are very real. Both of these individuals, one a friend, the other an acquaintance, lost jobs due to economic downturns at their respective organizations and both have taken jobs, simply to pay the bills, while they seek out new opportunities in their chosen professions.
Both of these individuals are examples of many that have succumbed to a massive, but hidden, problem called underemployment. Watching falling unemployment numbers now being reported below 6%, down from nearly 10% four years earlier is, in many ways, simply misleading.
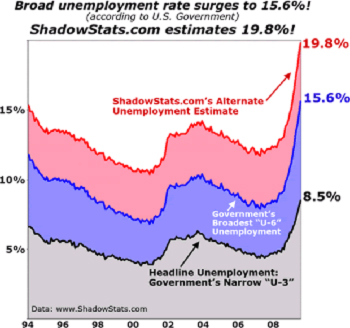
I believe it was Mark Twain who quipped, “statistics are like an alienist; they can work for either side.” The ‘official’ unemployment rate (technically called U3) is a simple and broad measurement that divides the number of people who are not working, want to work, and have been actively applying for jobs by the sum of the people working and those loosely defined as unemployed. In doing so, today, you get a number that’s just below 6% as stated above. While many seem to accept this as THE measurement of employment health, this is merely one measurement though; The unemployment rate can be calculated using a variety of differently ‘useful’ parameters and the U3 rate leaves out many that should be included as they are in the U6 statistic (see below).
With the Fed preparing to raise interest rates as soon as they believe the labor market is strong enough, determining that strength is difficult. But one fact everyone should be able to reasonably agree on is that the ‘official’ unemployment rate does not even attempt, and can’t really, measure the actual strength or health of the labor market exemplified by the openly known fact that Fed Chair Janet Yellen looks at a “dashboard” of at least nine labor market indicators!
Thus, lots of people who are unemployed by many reasonable definitions may not count as such, depending on the metrics used, in the official government statistic. In fact, using the government’s own definition, workers who are discouraged or marginally attached to the labor market do not count in the official unemployment rate. There are different, broader, unemployment measures available, but they do not get the headlines.
In fact, of the over 90 million Americans 16 years old or older that are not working, hence not part of the equation, fall into several categories: retirees, stay-at-home parents, students, and those who would prefer working but have given up on finding a job. Policy makers have been reduced to making educated guesses about the relative size of each subgroup of those not working because the capture of the actual numbers is speculative at best, and then their potential to reenter the labor market as conditions improve remains in question too.
Despite the significant decrease in the official U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) unemployment rate, the ‘real’ unemployment rate is most likely over double that approaching near 13%. This number, which is a better portrait of the nation’s REAL economic health, reflects the government’s U-6 report, which accounts for the full unemployment picture, and this includes those that are marginally attached (describes individuals not currently in the labor force who wanted and were available for work)to the labor force, plus those “employed part time for economic reasons.” In July, this marginally attached group accounted for 2.2 million people. To put that in perspective, there are currently 16 states in the U.S. with populations smaller than 2.2 million. Another number, large in and of itself is the 741,000 discouraged workers – workers not currently looking for work because they believe no jobs are available for them. These are included within the list of marginally attached people. Another 7.5 million were not considered unemployed because they were employed part-time for economic reasons. Those people are also called involuntary part-time workers – working part-time because their hours were cut back or because they were unable to secure a full-time job.
Unemployment is really a measure of labor market disequilibrium; it measures the mismatch between employers’ demand for labor of various types and workers’ willingness and ability to supply that labor. Unemployment that is “too high” or “too low” in aggregate, or in specific job categories, is really about these mismatches, not the overall health of the labor market.




Please Share Us!